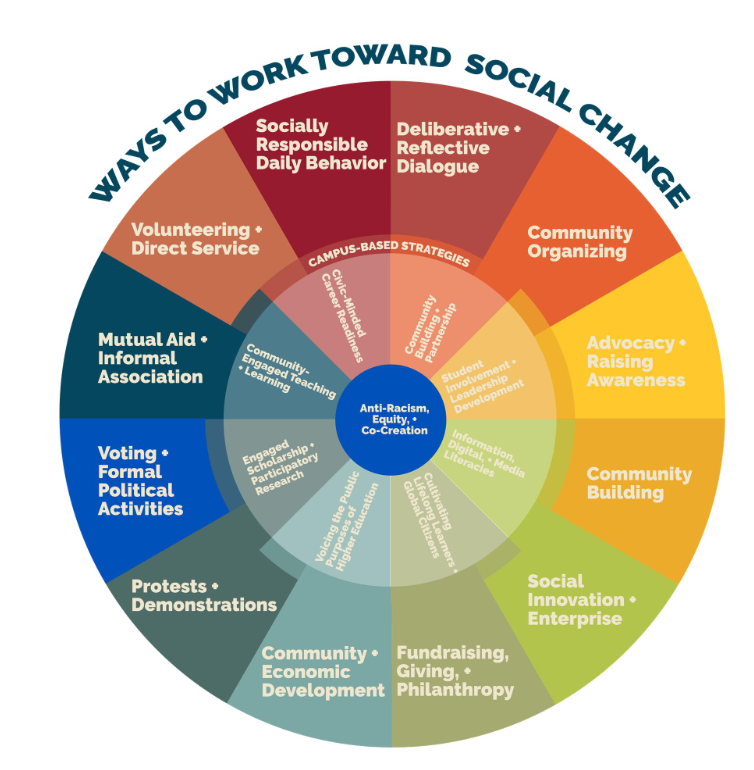
Social Change Wheel 2.0
The Social Change Wheel 2.0, from the University of Minnesota’s Campus Compact, highlights ways to engage in social change, bringing the pieces together with the work of higher education institutions. The Social Change Wheel 2.0 begins in the center with anti-racism, equity, and co-creation as guiding principles. The middle ring suggests a range of campus-based strategies in civic and community engagement. The outer ring encompasses a range of engagement approaches happening both inside and outside of a higher education setting.
For those seeking to engage in change, the first step is figuring out how we can engage, the next step is considering who needs to be involved – and why. Then you are ready to determine what needs to be done to take action. Important considerations for engaging include: Are we including those who are directly experiencing the issue? Do we have those with the influence, responsibility, and/or knowledge to change conditions? Does the environment encourage and allow effective and meaningful engagement?
Engagement by Strategies
Purposeful and meaningful engagement exists at every level (individual, relationship, community, societal). Thinking through these levels can help us find opportunities for engagement or action. Engagement may vary for those in different positions, roles, or levels. However, anyone and everyone can engage in social action. Here are ways to think through opportunities for action.
| Social Change Wheel - Ways to Engage | |
|---|---|
| Socially Responsible Daily Behavior: | Partaking in public life or civic responsibility, building on personal cultural competence, standing up for the marginalized. |
| Deliberative and Reflective Dialogue: | Saving space to hear the stories of marginalized people, engaging in public dialogue around a particular issue, partaking in opportunities to learn stories of others. |
| Community Organization: | Bringing people together (across community sectors) to work towards a common vision, mission, or goal. |
| Advocacy and Raising Awareness: | Collecting of evidence of an issue and supporting change for the issue through public and private communication. |
| Community Building: | Building capacity of those who live in the community to sustain meaningful action to support overall health of the community. |
| Social Innovation/Enterprise: | Providing sustainable solutions to social problems as organizations. |
| Fundraising, Giving, Philanthropy: | Donating time, service, money, or goods to a community or non-profit organization. |
| Community and Economic Development: | Providing resources or economic opportunities to sustainably improve social conditions. |
| Protests and Demonstrations: | Participating in rallies, creating art, or other publicly visible expressions of political or social messages. |
| Voting/Formal Political Activities: | Participating in voting activities, mobilizing others to participate, and influencing public policy. |
| Mutual Aid/Informal Association: | Bringing people together to act collectively for a common goal. |
| Volunteering and Direct Service: | Addressing needs by providing service/assistance through organizations such as schools, churches, social service agencies, and non-profits. |
Level of Participation
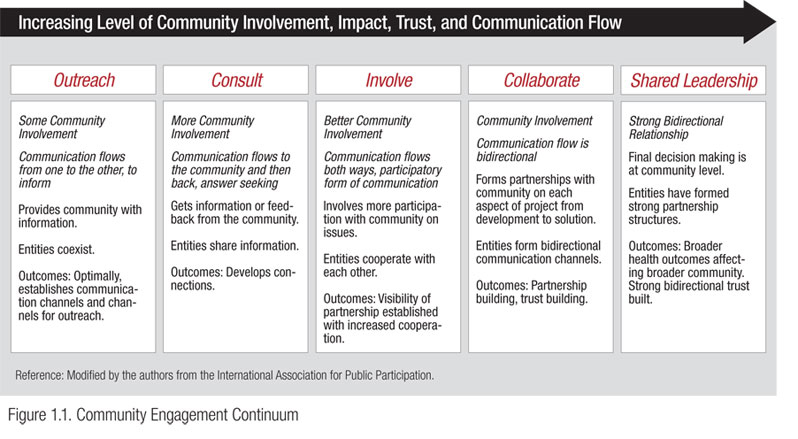
Moving from left to right on the diagram reflects movement towards a more community-engaged approach.
Pathways to Service
”Pathways to service” describe the variety of ways people can use their knowledge, skills, and talents to improve their communities. We all bring something different to our communities. Many of the pathways overlap, allowing our diverse experiences to help us determine which pathways are the best fit.
| Pathways to Service | |
|---|---|
| Volunteer | Works with those in need of assistance or addresses a need of the broader community. Examples:
|
| Advocate | Creates awareness and action on issues that impact the community. Examples:
|
| Policy Shaper | Influences and shapes decisions for the public interest through policies and laws. Examples:
|
| Researcher | Gathers and presents findings that inform action on issues that affect the community. Examples:
|
| Social Innovator | Uses knowledge and skills to create ideas and strategies that address social issues. Examples:
|
Resources on Engagement
- Kansas Healthy Communities Action Toolkit – Engagement
- The Social Change Wheel 2.0 Toolkit (pdf)
- Social Change: Everyone Has a Role to Play